A holistic understanding of risk
Governance is key in the enterprise – a holistic and permeating understanding and management of risk in your organization. It’s not a series of boxes to be checked – each member of your tech team needs to be able to evaluate the possible impact of their actions on the project, tools, or cloud. Of course, Cycloid’s here to offer you some help and guidance.
Infra Import allows you to rapidly industrialize your deployments by automatically creating IaC
Infra Import is our infrastructure-as-code generator based on open-source tool, TerraCognita. It connects to your manually-deployed cloud infrastructure and automatically creates your Terraform file and related Git modules, helping you modernize and scale your business in a reproducible and controlled manner.
Multiple organizations
If you manage multiple organizations that are completely siloed, Managed Services/Business Unit View is the tool you need. A single, centralized hub allows you to structure these multiple units in the way that makes the most sense for your team, then manage them from an efficient and streamlined console.
Governance and flexibility
The framework allows those with responsibilities for tools and cloud to ensure everyone’s rights are directly related to their job. These features pre-define minimal privilege, ensuring governance but allowing exactly the right amount of flexibility individuals need to do their job. To do this, Cycloid uses industry-standard Open Policy Agent (OPA), which means you can define roles and deploy policies with confidence.
Enterprise
Cycloid’s tools work for any organization, but offer specific features that make them particularly efficient for the enterprise level. The framework can be used as a SAAS or on-premise, depending on the governance requirements of your organization. You’ll also be able to plug Cycloid into any existing tools you use, such as OpenID, SAMLv2, and AzureAD.
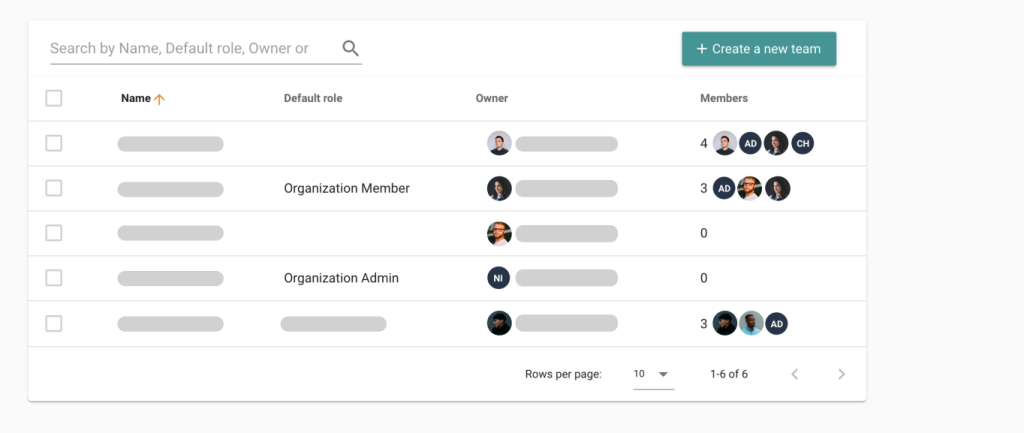
Teams and custom roles
As you delve deeper into Cycloid’s tools and features, you’ll see that we’ve made it easy for you to establish the principle of least privilege throughout everything your tech team does. Cycloid allows you to set the limits and standards (in terms of teams, roles, and policies) you expect your techs to maintain throughout their dealings with the project.
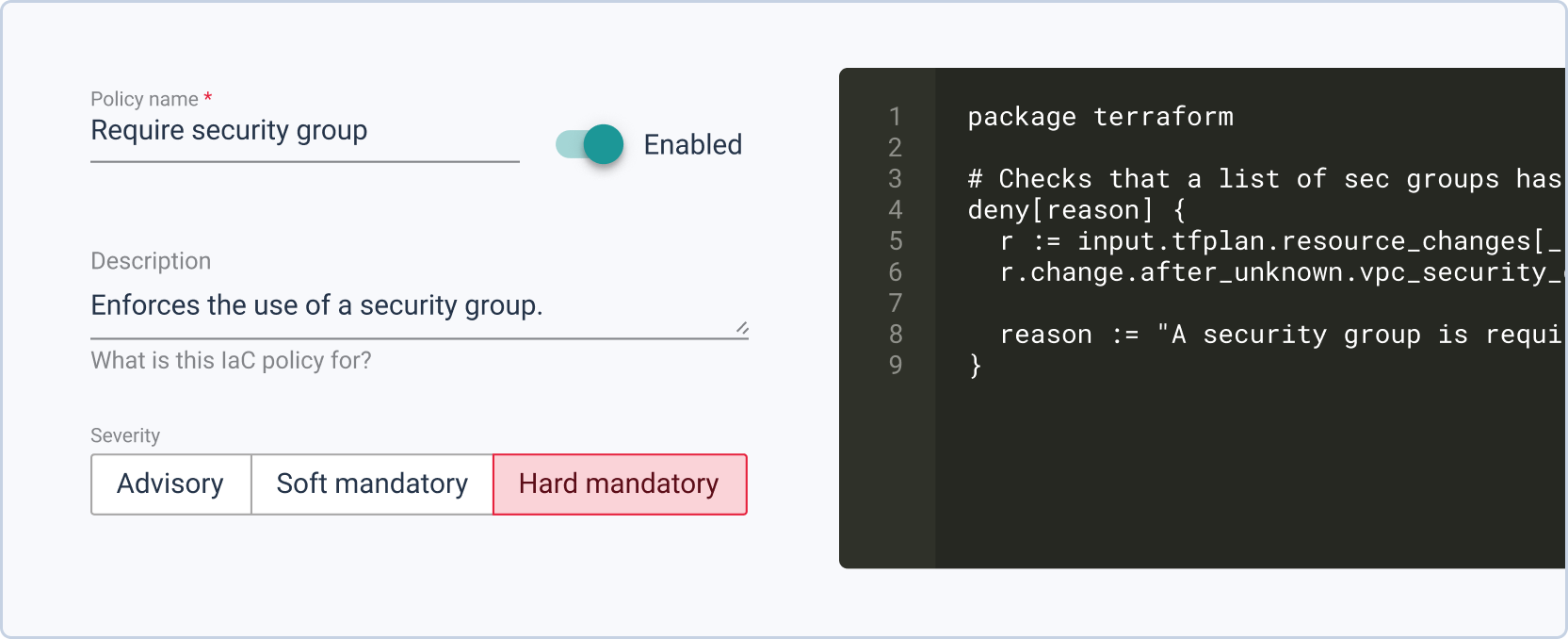
InfraPolicies and more
InfraPolicies are a TerraForm-based implementation of Policy as Code that provide fine-grained control over changes to an organization’s infrastructures while simultaneously defining validation rules. Later on, tools like StackForms and TerraCost will allow you to define limits that are automatically deployed, freeing your ops from watchdog duties and preventing inadvertent problems.
Cycloid for Governance, Security, and Compliance
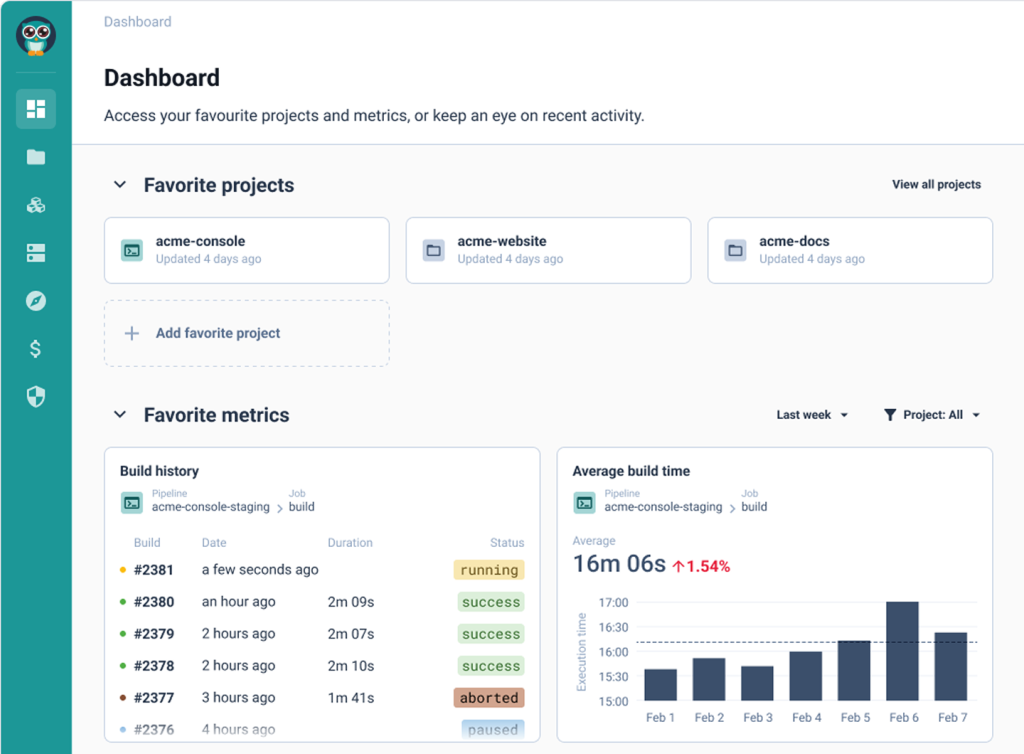
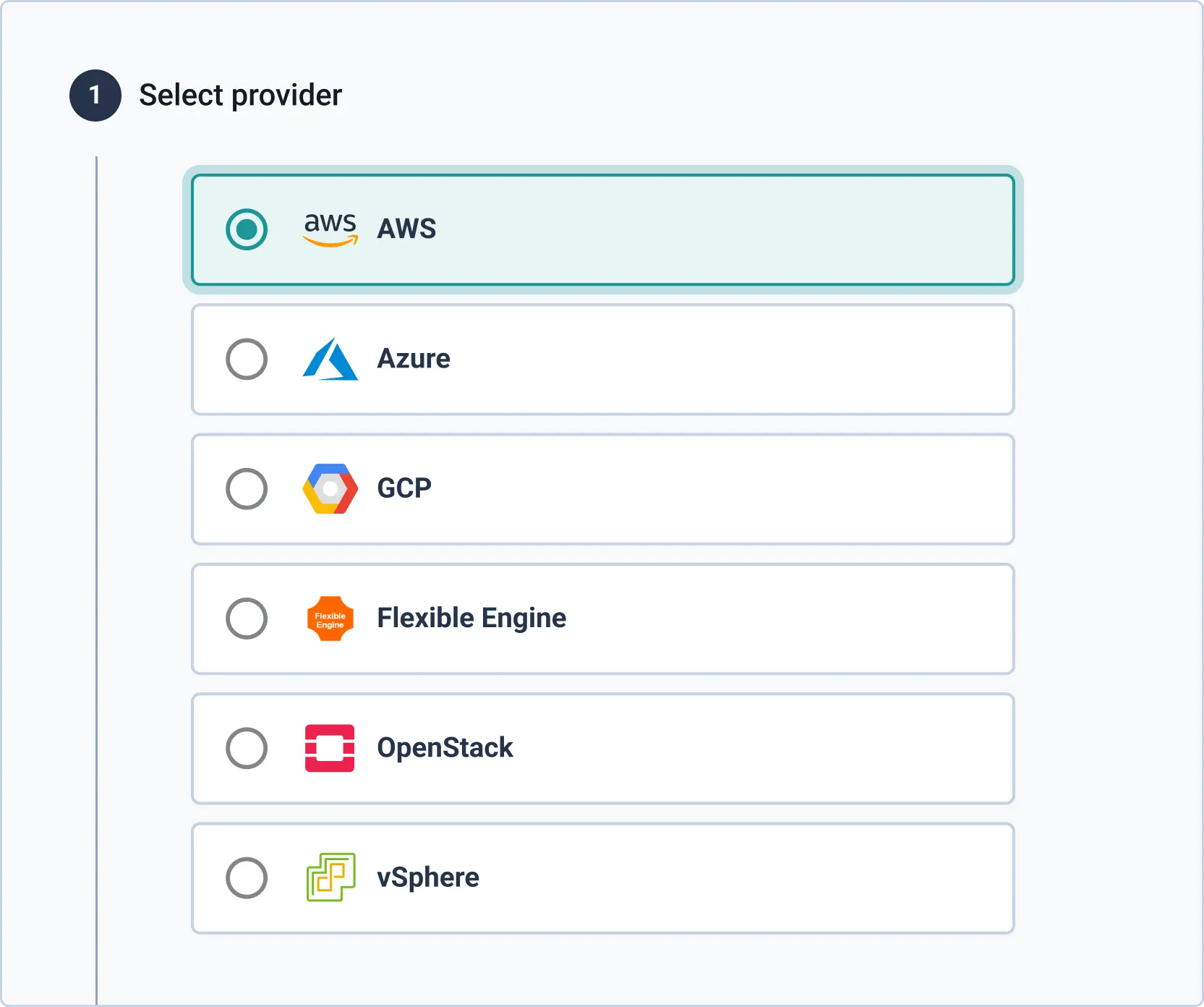
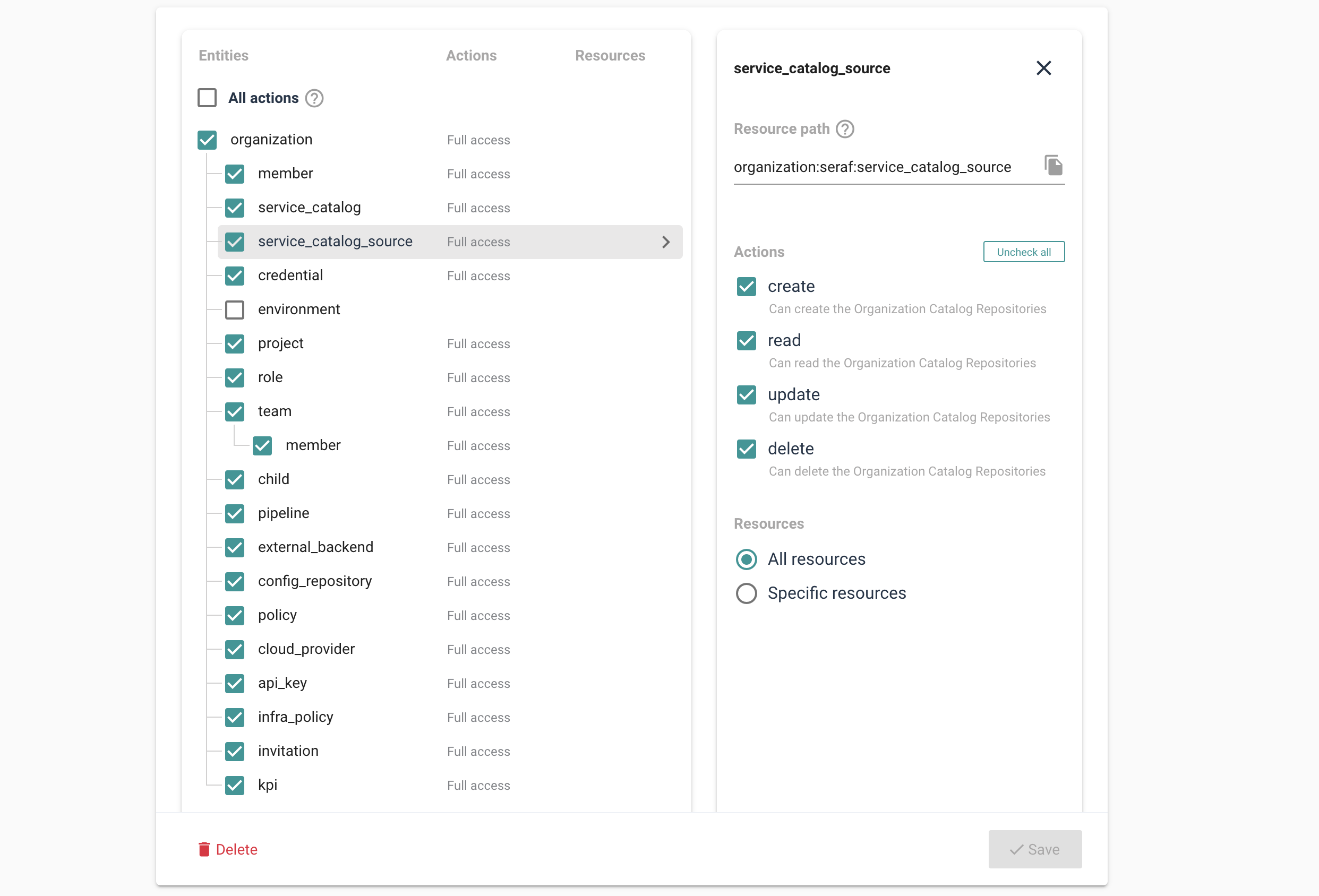
Hi. In this video, we are going to review how Cyclit platform engineering can help you to bring governance, security, and compliance to your organization. Cyclic platform engineering expose this kind of catalog of services to do to your end users, including developers in use cases such as CMP and IDP. But you want to expose this kind of automation in a controlled manner with governance, with security, with compliance. So the first thing I want to emphasize here on this topic is that you can deploy and host Cycloid platform engineering on premises or in your cloud providers of choice. So you can definitely look at the change log and define when do you want to upgrade the platform yourself. And it can be also air gapped if you want to. But before we move forward, I would like to go through some basic concept of Cycloid. So first of all, Cycloid is a multitenant platform. We call each tenant an organization and in each organization you will invite different users and, eventually they can be authenticated through your identity providers such as Microsoft Entra ID for example, through SAML or OpenID Connect. And each organization will have also a set of stacks and that will constitute the service catalog that the user will be able to consume. Each stack is actually version control in your git. Okay. So all the catalog of services is version control in your git and Cyclery is going to read your git to expose the catalog of service in the portal. In terms of consumption, the user will actually, first of all, create what we call a product, which is basically a business application. It can be a website or web application. And then in each project, you will have one or several environments. So it can be production, it can be staging. Or if the user is a developer, it can also be, testing, a pull request, for example. And then in each environment, you will have one or several components, which is really where the automation is executed to do something, to deploy some infrastructure, to deploy some application, to manage some container. So it's really a wide possibility in terms of automation that you can run here. What you can see here is stack form auth configuration and this is where the end user is going to define the desired configuration according to, the web form that has been designed by your platform team. So the design is going to be stored in the stack, but the values that the end user fill in is going to be stored in the git config. This is also your git. Okay. So both of them are your git. So this is for the repeatable automation, the stacks. These are for the desired configuration of each of the deployments. And, optionally, you can have also the management of Cloud Bucket to store your Terraform state file. So Cyclery can act as an HTTP Terraform, backend endpoint. And, Terraform state file will be persisted in a cloud bucket such as an s three bucket or a container on Azure or a cloud bucket on GCP, for example. Okay. So now that we have reviewed the basic concept of Cycloid, let me go through a quick demo. So first of all, the organization are organized hierarchically. So that means if I go, for example, on this organization, I can see I have sub organization. So it's just to get a better organization so we can have a business unit, for example, maybe some departments and maybe another layer of teams, let's say. So if I go for this organization then you have a couple of settings here for each of the tenants. So first of all you can integrate with an identity provider such as, Entra ID. You can enforce multi factor authentication. You can, of course, configure a remote back end. So that's exactly what I just said. So you can configure your S3 bucket or, GCP Cloud bucket as the remote back end to persist your Terraform state file. And you can configure also the white label portal here. So to customize your color your logo and, colors, to adapt to your branding. Okay. So that is to set up your tenant, your organization. But now what about the users? What can they do in this tenant once they get invited? Of course, people will just consume the catalog of services, and they will not really care about security, about managing the the credentials, and managing the the roles, for example, and more advanced things like that. So that's where the role based access control comes into play. So to configure roles, you go to security and roles. And here you can see you have a couple of default roles, which are generally enough to start with, but you can also add custom roles as well. So if you want, for example, a role that can, manage the roles, exactly what we are doing here, you can check this one and then say in a crude manner what are the actions that are allowed, for for, for this role. Okay. So maybe I can, do everything or I can, just, read, for example, the the role. So you can decide what is the actions, on that item. Of course, you have same thing for a credential to manage the service catalog, to manage the policies that's more for compliance, the I API keys, and so on. So once you have created your role according to the different position you will have in your team, you want to go to the organization settings here. And you want to assign these roles eventually directly to people, but, in general, that's not the best practice. What you want to do is more to assign to different teams. We call it teams, but it's actually a group of users. So if I go to the operations team, you can see that all these people, they will actually inherit finance admin and organization admin because it is a operation. They have full control, on this, tenant. So we have seen, how to set up multi tenancy, configuring the organizations, inviting users through Entra ID, for example, and then assign roles with the role based access control modules so each of the user can actually do their job in full autonomy no more no less. Now we can review how a user will actually work and see a project for example. So if I go to project here in this organization and I will go to my demo app. If you remember, this is the business application. I have here a dev environment for because I am a developer. And here I have a staging environment because I want to deploy a released application, which is a node application. In that case, this is going to deploy infrastructure and application at once. This is more for developer that, will, manage, you know, snapshot of database, scaffold git repository, and test a PR, for example, from that git repository. So that's the different components as we have seen before. And last but not least, we have also an observability. So it's important to control, but it's also important to, observe. So we can see here with the audit logs who has done what. And eventually, you can also, go to the pipeline overview. So here you can see the different pipelines that are running. If something becomes orange or red, of course, you need to check what's going on. I hope you like this video. This is, how you can govern and ensure security and compliance, in your organization using Cycloid. Have a good day.
Put your people in control, make software delivery more efficient, manage your cloud costs – and help the planet with our sustainable Platform Engineering platform.